💻 The Advantages of Implementing Mobility Data Specification (MDS) 2.0
MDS 2.0 enhances how cities oversee shared mobility by improving safety, streamlining data collection, and supporting emerging transport modes. Discover how it empowers smarter, more responsive urban mobility management.
%20copy.png)
📩 Stay updated on industry trends & Vianova product updates—subscribe to our Newsletter here!
Introduction
The rise of shared mobility services, such as e-scooters, bikes, and ride-hailing, has brought about new complexities in urban transportation management. Cities are now tasked with integrating these services into their existing infrastructure while ensuring safety, efficiency, and equity for all users.
In response to these challenges, the Mobility Data Specification (MDS) has emerged as a vital tool for cities to effectively manage and regulate these new forms of transportation. MDS fosters a collaborative approach, acting as a "two-way street" for communication and data sharing between public agencies and private mobility providers.
This collaborative framework allows cities to leverage real-time data to make informed decisions and adapt policies dynamically, ensuring a responsive and efficient transportation system. This blog delves into the advantages of implementing MDS 2.0, with a particular focus on the insights cities can gain and the diverse modes of transportation it supports.
What is MDS 2.0?
MDS 2.0, a project of the Open Mobility Foundation (OMF), is a sophisticated set of application programming interfaces (APIs) that streamlines the exchange of data between cities and mobility providers. While the OMF currently manages MDS, it was initially developed by the Los Angeles Department of Transportation in 2018.
%20copy.png)
With the primary goals of simplifying the specification and enhancing its flexibility, MDS 2.0 standardizes data formats, enabling cities to gather real-time information on the location, status, and usage of shared mobility services. This standardization not only facilitates data collection but also promotes a collaborative approach between cities and mobility providers, creating a "two-way street" for communication and cooperation.
Improving Safety with MDS 2.0
MDS 2.0 plays a crucial role in enhancing the safety of shared mobility services. By providing cities with real-time data and communication channels, MDS 2.0 empowers them to:
- Enforce Speed Limits: Cities can utilize MDS 2.0 to establish and enforce speed limits for shared mobility vehicles in designated areas, such as school zones or areas with high pedestrian traffic. This capability ensures that vehicles operate at safe speeds in sensitive locations.
- Manage Parking: MDS 2.0 enables cities to designate specific parking zones for shared mobility vehicles. This organized approach reduces clutter on sidewalks and streets, minimizing the risk of accidents and improving pedestrian safety.
- Monitor Compliance: With MDS 2.0, cities can effectively monitor compliance with various regulations, such as helmet requirements or operating hours. This real-time monitoring capability allows for prompt intervention and ensures that shared mobility services adhere to safety guidelines.
- Respond to Events in Real-Time: MDS 2.0 empowers cities to make real-time policy changes in response to events and accidents. This dynamic capability allows for immediate adjustments to address safety concerns and ensure a swift response to unforeseen circumstances.
Enhanced Data Collection and Analysis
MDS 2.0 empowers cities to collect a wide range of data, providing valuable insights into shared mobility usage and patterns:
- Real-time Location Data: Cities can track the precise location of shared mobility vehicles, such as e-scooters and bikes, in real-time. This data enables cities to monitor compliance with parking regulations, identify areas with high demand, and optimize infrastructure planning to accommodate these services effectively.
- Trip Data: MDS 2.0 allows cities to collect comprehensive data on trip origins, destinations, and durations. This information is crucial for understanding travel patterns, identifying popular routes, and assessing the impact of shared mobility services on public transportation. These insights can inform policy decisions and infrastructure development to improve overall transportation efficiency.
- Vehicle Status Data: Cities can access real-time data on the status of shared mobility vehicles, including battery levels and maintenance needs. This information helps ensure the availability and reliability of these services, minimizing disruptions and enhancing user experience.
Increased Efficiency and Reduced Costs
Implementing MDS 2.0 offers significant efficiency gains and cost reductions for cities:
- Automating Data Collection: MDS 2.0 automates the process of collecting data from mobility providers, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing administrative burden. This automation frees up valuable staff time and resources for other tasks.
- Optimizing Resource Allocation: By analyzing usage patterns and demand, cities can optimize the allocation of resources, such as parking infrastructure or charging stations. This data-driven approach ensures that resources are strategically placed to maximize their utilization and minimize waste.
- Improving Enforcement: Real-time data from MDS 2.0 enables cities to improve enforcement efforts, reducing the time and resources spent on manual inspections. This efficient approach allows for targeted enforcement and ensures compliance with regulations.
- Reduced Operating Costs: MDS 2.0 streamlines data collection and analysis, leading to significant reductions in operating costs and staff time. This cost-saving benefit allows cities to allocate resources more effectively and invest in other critical areas of urban development.
Support for New Modes of Transportation
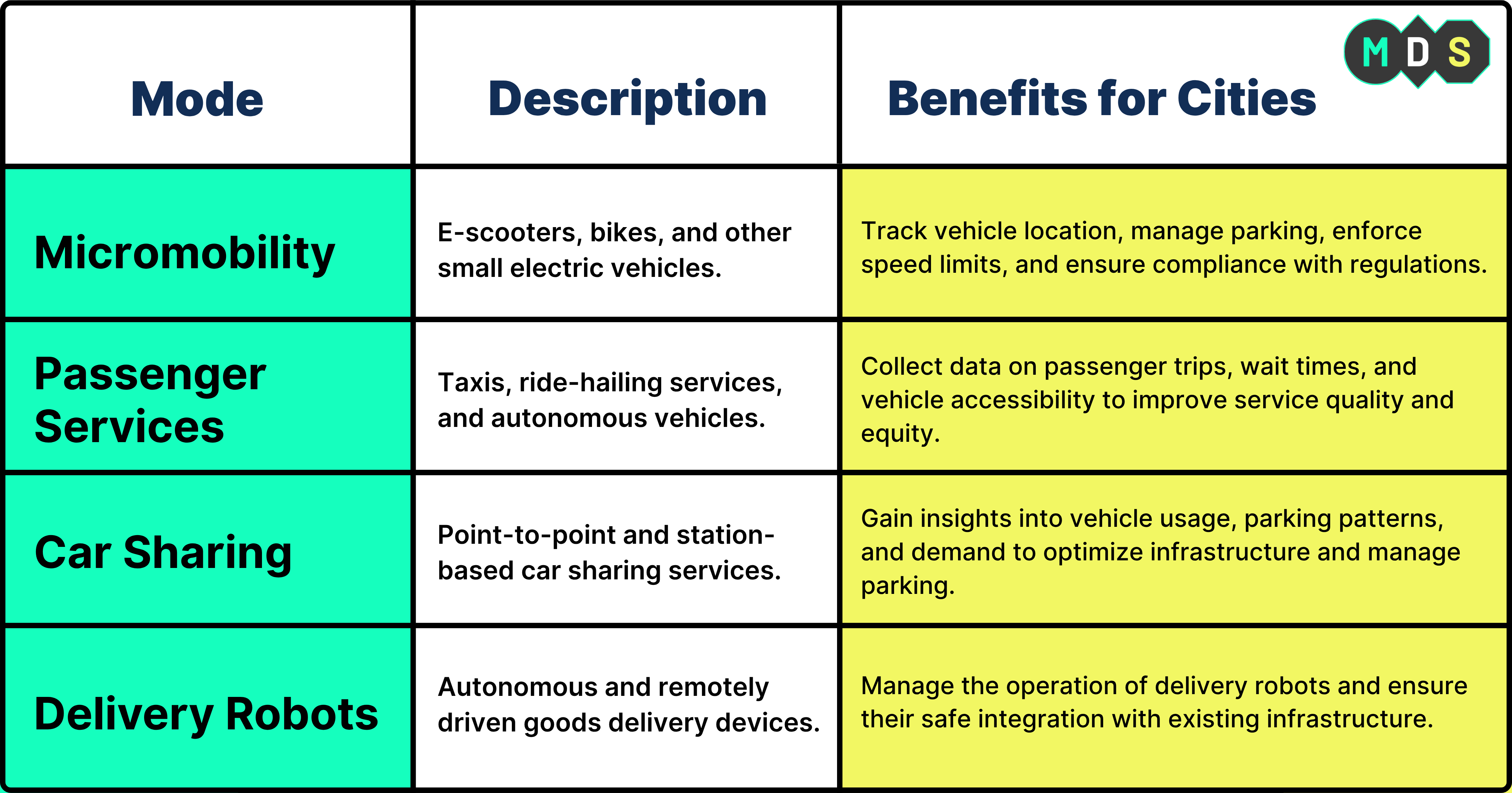
MDS 2.0 is designed with flexibility in mind, ensuring its adaptability to new and emerging modes of transportation. Beyond e-scooters and bikes, MDS 2.0 supports:
- Passenger Services: This encompasses various modes of transportation, including taxis, ride-hailing services, and autonomous vehicles. MDS 2.0 enables cities to collect data on passenger trips, wait times, and vehicle accessibility, providing valuable insights into the performance and equity of these services.
- Car-sharing: MDS 2.0 supports data collection from car-sharing services, offering insights into vehicle usage, parking patterns, and demand. This data helps cities understand the impact of car-sharing on urban mobility and optimize infrastructure accordingly.
- Delivery Robots: As delivery robots become increasingly prevalent in urban environments, MDS 2.0 provides a framework for cities to manage their operation and ensure their safe integration with existing infrastructure. This proactive approach allows cities to address potential challenges and maximize the benefits of this emerging technology.
- Emerging Modes: MDS 2.0 is a forward-looking specification, enabling cities to regulate emerging modes of transportation like autonomous robot deliveries. This adaptability ensures that cities can effectively manage the evolving landscape of urban mobility and integrate new technologies seamlessly.
To illustrate the diverse applications of MDS 2.0, the following table provides a detailed overview of the modes of transportation it supports:
Data Privacy and Security Implications of MDS 2.0
While MDS 2.0 offers numerous benefits, it's essential to address the data privacy and security implications associated with its implementation. MDS 2.0 prioritizes data privacy by excluding personal information about riders, such as names or payment details. The specification focuses on collecting vehicle-level data, such as location and status, to minimize privacy risks.
However, cities must implement appropriate data security measures to protect the information collected through MDS 2.0. This includes establishing clear data retention policies, utilizing secure data storage systems, and adhering to relevant privacy regulations. The OMF provides valuable guidance to cities on best practices for data privacy and security in the MDS Privacy Guide for Cities. By following these guidelines and implementing robust security measures, cities can ensure the responsible and ethical use of MDS 2.0 data.
Case Studies of Cities Implementing MDS
Several cities have successfully implemented MDS, demonstrating its practical benefits in real-world scenarios:
- Los Angeles: As the pioneer of MDS, Los Angeles utilizes the specification to manage its dockless mobility program, which encompasses e-scooters and bikes. MDS data has been instrumental in helping the city understand usage patterns, enforce parking regulations, and improve safety for all road users. The city's experience showcases the effectiveness of MDS in managing the complexities of shared mobility services.
- Santa Monica: Santa Monica has also embraced MDS to manage its shared mobility program. The city leverages MDS data to track vehicle locations, monitor compliance with regulations, and make data-driven decisions about infrastructure improvements. This proactive approach has enabled Santa Monica to integrate shared mobility services seamlessly into its transportation network.
- Seattle: Seattle employs MDS to enhance transportation planning and safeguard against the misuse of personal mobility data. The city's focus on data privacy and responsible data use highlights the importance of ethical considerations in implementing MDS.

Conclusion
MDS 2.0 has emerged as an indispensable tool for cities navigating the complexities of shared mobility services. By standardizing data collection and communication, MDS 2.0 empowers cities with the insights needed to improve safety, equity, and efficiency in their transportation systems. The specification's flexibility and support for new modes of transportation ensure that cities can adapt to the evolving landscape of urban mobility and integrate new technologies seamlessly.
While the benefits of MDS 2.0 are undeniable, cities must also consider the potential challenges associated with its implementation. These challenges include the need for robust data security measures, the development of clear data governance policies, and the allocation of resources for data management and analysis. However, the long-term benefits of improved transportation planning, enhanced safety, and increased efficiency outweigh these initial challenges.
For cities considering the adoption of MDS 2.0, it is recommended to start with a pilot program focusing on a specific mode of transportation or geographic area. This phased approach allows cities to gain experience with MDS 2.0, assess its effectiveness, and refine their implementation strategies before scaling up to a city-wide deployment. By carefully planning and executing their MDS 2.0 implementation, cities can unlock the full potential of this valuable tool and create a more sustainable, efficient, and equitable transportation future.
About Vianova
Vianova is the data analytics solution to operate the mobility world. Our platform harnesses the power of connected vehicles and IoT data, to provide actionable insights to plan for safer, greener, and more efficient transportation infrastructures.
From enabling regulation of shared mobility to transforming last-mile deliveries, and mapping road risk hotspots, Vianova serves 150+ cities, fleet operators, and enterprises across the globe to change the way people and goods move.
Ready to learn more? Visit our page to get in touch.
👉 Read our previous blog here!
Become part
of the movement
in the Vianova world.
Let's get in touch
Lets talk! We are excited to hear how we can help you solve your mobility challenges.





